
For more learning, CFI offers a wide range of courses on financial analysis, as well as accounting, and financial modeling, which includes examples of the marginal cost equation in action. Johnson Tires, a public company, consistently manufactures 10,000 units of truck tires each year, incurring production costs of $5 million. Begin by entering the starting number of units produced and the total cost, then enter the future number of units produced and their total cost.

Economies of Scale (or Not)
As we can see, Marginal Cost can be significantly impacted by external factors, such as a surge in demand for materials. When the marginal social cost of production is less than that of the private cost function, there is a positive externality of production. Production of public goods is a textbook example of production that creates positive externalities. An example of such a public good, which creates a divergence in social and private costs, is the production of education.
- The quantities involved are usually significant enough to evaluate changes in cost.
- In economics, marginal cost is the change in total production cost that comes from making or producing one additional unit.
- The firm’s production function tells us how much output the firm will produce with given amounts of inputs.
- Instead of investing in minimally successful goods, it can focus on making individual units that maximize returns.
- It is not the cost per unit of all units produced, but only the next one (or next few).
3 Costs in the Short Run
The marginal cost line intersects the average cost line exactly at the bottom of the average cost curve—which occurs at a quantity of 72 and cost of $6.60 in Figure 7.8. The reason why the intersection occurs at this point is built into the economic meaning of marginal and average costs. The point of transition, between where MC is pulling ATC down https://www.bookstime.com/ and where it is pulling it up, must occur at the minimum point of the ATC curve. The breakdown of total costs into fixed and variable costs can provide a basis for other insights as well. The first five columns of Table 7.10 duplicate the previous table, but the last three columns show average total costs, average variable costs, and marginal costs.
What is Marginal Cost in Economics?
Marginal cost is the additional cost that an entity incurs to produce one extra unit of output. In other words, it is the change in the total production cost with the change in producing one extra unit of output. Let us learn more how to get marginal cost about the marginal cost along with its formula in this article. It would be as if the vertical axis measured two different things. Using the figures from the previous example, the total cost of producing 40 haircuts is $320.

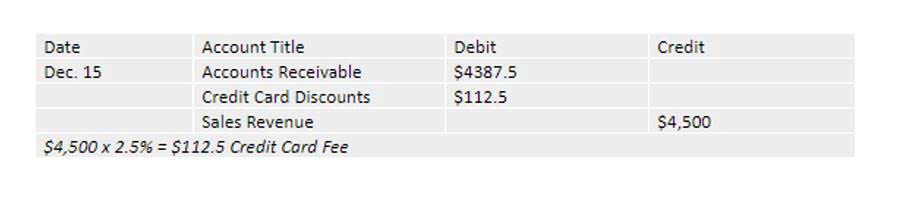
Given below is the data of the total cost of production of a firm producing school uniforms. We will be finding the marginal cost by observing the changes in the total cost and in the output produced. Based on this value, it may be easier to decide if production should increase or decrease. You may find a marginal cost calculator under different names, such as an incremental cost calculator or a differential cost calculator, but they are all related to the same topic. However, marginal cost is not the same as margin cost described in our margin calculator! In this article, you can find more details on how to calculate the marginal cost and the marginal cost formula behind it.
Negative externalities of production
Short run marginal cost
- Your additional cost of producing one extra product depends mostly on the value of the product itself – materials, workers’ wages, etc.
- But in either case, this kind of profit optimization is mostly theoretical, as there are often many factors preventing businesses from doing so in the real world, such as competitive dynamics and imperfect information.
- The point of transition, between where MC is pulling ATC down and where it is pulling it up, must occur at the minimum point of the ATC curve.
- Marginal cost is reflective of only one unit, while average cost often reflects all units produced.
- It is an important concept in cost accounting, as marginal cost helps determine the most efficient level of production for a manufacturing process.
- To calculate marginal cost, divide the change in cost by the change in quantity of the particular product or service.
